Large flow release control device for flammable refrigerant
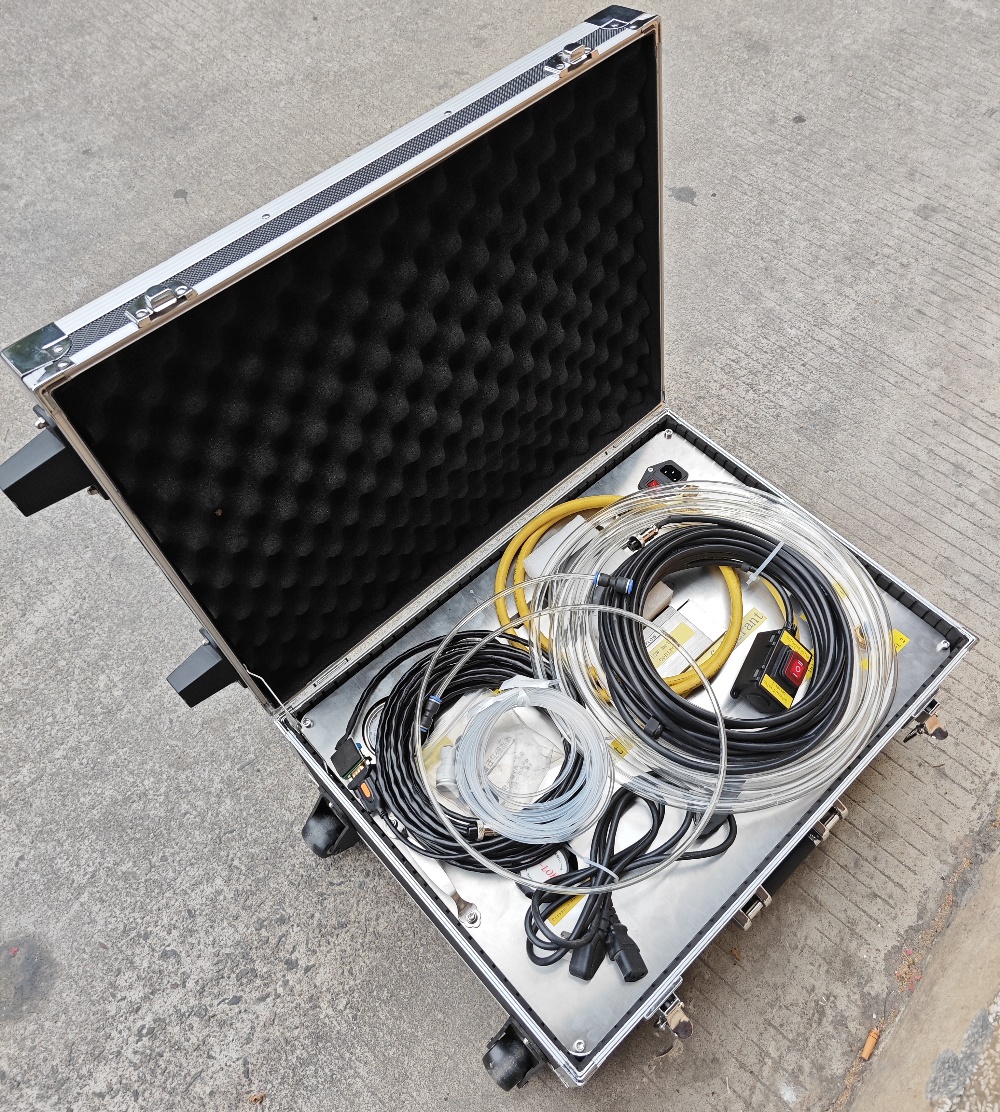
Portable hand-held box structure, flammable refrigerant simulated refrigerant leakage refrigerant flow control device. High control and fast response time. No need to use electronic scale to control refrigerant leakage rate. Can be remotely controlled to better protect the safety of operators.
Description
This device is designed based on the requirements of the household air conditioning product safety standards IEC 60335-2-40, GB 4706.32, and UL 60335-2-40. Its purpose is to control the refrigerant leakage rate when simulating refrigerant leakage tests in Annex FF, Annex MM, and Annex PP of the household air conditioning product safety standards.
Common refrigerants for air conditioners are R32, R290, and R454B. If it is the Annex MM test , the leakage rate is as follows:
| Annex MM | |||
| Type of Refrigerant | leak rate (g/s) | constant(4) | LFL |
|---|---|---|---|
| R32 | 1.228 | 4 | 0.307 |
| R454B | 1.228 | 4 | 0.307 |
| R290 | 0.152 | 4 | 0.038 |
| The UL 60335-2-40 standard has different LFL values, so we will not calculate them here because the values do not change much. | |||
If the Annex FF is followed, the refrigerant release amount and leakage rate will be relatively high. We have selected several values of releasable quantity as examples for calculation:
| Type of refrigerant | mff (kg) | refrigerant capped quantity limit | leak rate (kg/s) | leak rate (g/s) | leak rate (L/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R290 | 0.152 | m1 | 0.0006333 | 0.633333333 | 19.3015873 |
| R290 | 0.304 | 2*m1 | 0.0012667 | 1.266666667 | 38.6031746 |
| R290 | 0.988 | m2 | 0.0041167 | 4.116666667 | 125.4603175 |
| R290 | 4.94 | m3 | 0.0205833 | 20.58333333 | 627.3015873 |
| R32/R454B | 1.842 | m1 | 0.007675 | 7.675 | 198.3692308 |
| R32/R454B | 3.684 | 2*m1 | 0.01535 | 15.35 | 396.7384615 |
| R32/R454B | 15.964 | m2 | 0.0665167 | 66.51666667 | 1719.2 |
| R32/R454B | 79.82 | m3 | 0.3325833 | 332.5833333 | 8596 |
The flammable refrigerants used in household air conditioners are basically R32 (for non-North American markets) and R454B (for North American markets), and most mobile air conditioners and dehumidifiers use R290. The traditional method is to use an electronic scale, through a needle valve or a multi-stage needle valve in series, to control the reduction of the weight reading of the electronic scale per unit time. This method is inconvenient to operate and has a large error; in the case of a large amount of refrigerant release, it is also prone to explosion danger; especially in the case of a large release, the accuracy of the scale used to weigh the large mass of the refrigerant tank is not enough.
The use of a high-precision gas mass flowmeter can solve this problem well.
The types of refrigerants that can be controlled by this device include R32, R290, R600a, R454B, R454C, R454A, R702, R717, R1234yf, R143a and most non-flammable refrigerants including R404A, R407C, R410A, R507A, R23, R22 R134a. In order to meet the requirements of some special mixed refrigerants, this device can edit the mixed gas by itself. It can edit 20 kinds of mixed gases. The percentage of various gas substances in each edited gas can be freely set. Five gases can be mixed at a time. In addition to conventional refrigerants, other refrigerants that can be controlled include acetylene, air, argon, isobutane, n-butane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, deuterium, ethane, ethylene, helium, hydrogen, krypton, methane, neon, nitrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, propane, sulfur hexafluoride, xenon, ammonia, butene, cis-butene, isobutylene, trans-butene, carbonyl sulfide, chlorine, dimethyl ether, hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen trifluoride, nitric oxide, propylene, silane, sulfur dioxide, trichlorofluoromethane, chloropentafluoroethane, hexafluoroethane, chlorotetrafluoroethane, pentafluoroethane, tetrafluoroethane, tetrafluoromethane, chlorodifluoroethane, trifluoroethane, difluorochloromethane, trifluoromethane, difluoromethane, Octafluorocyclobutane; also includes some breathing gases, barometric tube gases, fuel gas, chromatographic gases, laser gases, chimney gases, welding gases, oxygen concentrator gases, etc.
The control accuracy is ±0.8% of the reading and ±0.2% of the full scale. The control response time is 30–150 ms.
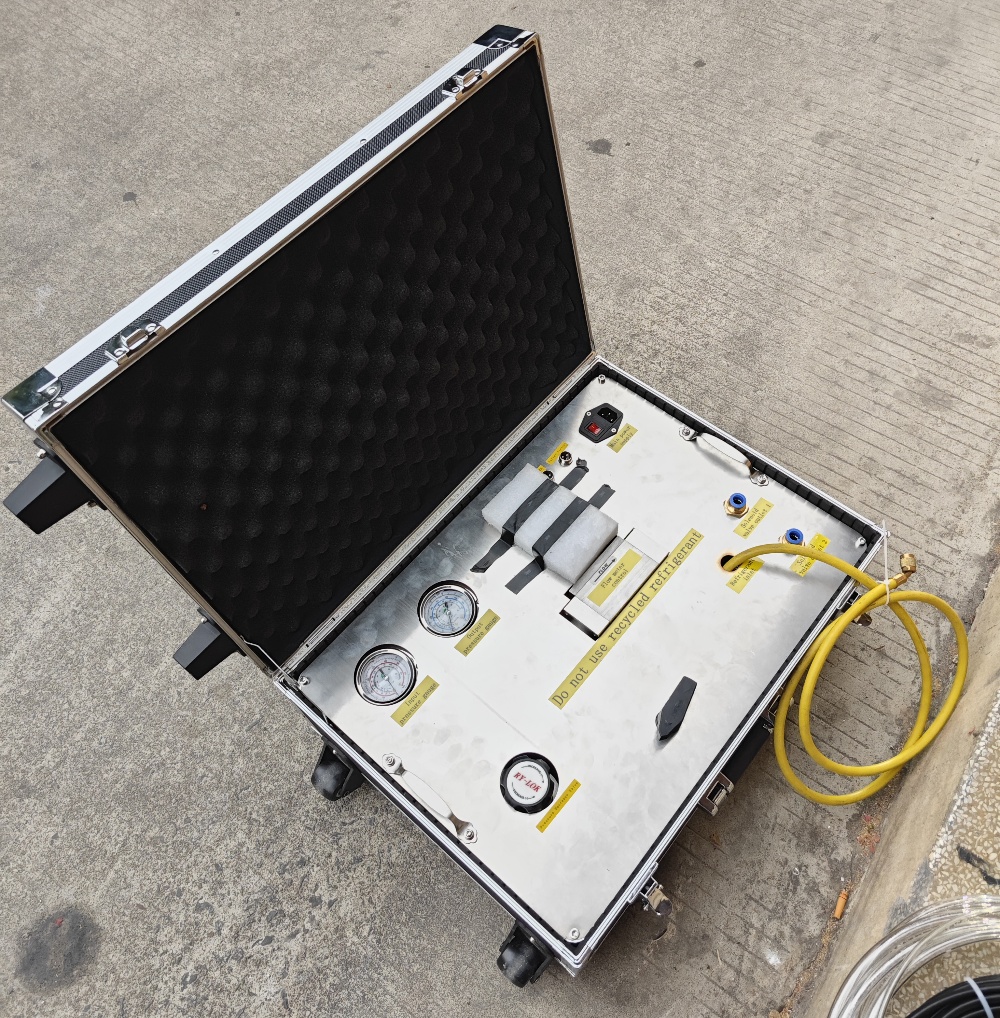
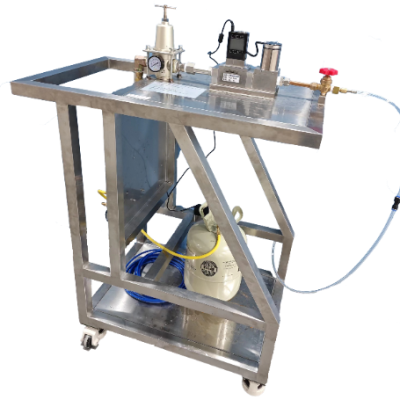
For easy operation, the device is integrated in a sturdy hand-towed box. The design of the hand-towed box can not only well protect its internal components, but also facilitate transportation and even on-site witness testing.
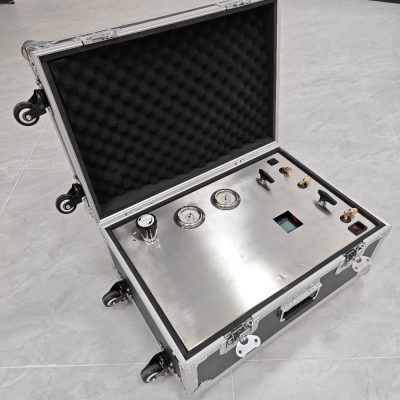
The device is equipped with a touch operation panel, and the interface diagram is as follows:
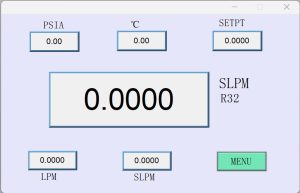
The user can directly select the type of gas to be controlled on the operation panel, set the controlled flow rate and observe the real-time flow rate on the system. The software can continuously monitor the flow rate, and the monitoring interval can be set; and the flow data obtained by continuous monitoring can be exported as a .csv file, which the tester can analyze.
Users can also install the control software on a personal computer and remotely control the equipment through the computer. Remote control can protect the operator very well, keeping the operator away from the area where the refrigerant is released, and reducing the harm to the operator in the event of an accidental explosion.
The internal electrical components of the instrument meet the explosion-proof requirements. The refrigerant supply connector (SAE 1/4″) equipped with the instrument are all conventional connectors for the air conditioning industry. It can be directly connected to the refrigerant tank for release operation. Because the release amount of refrigerant is relatively large, in the case of large release, it is necessary to select the SAE 3/4″ connector.
The flow rate can be displayed in g/s, L/min or mL/s.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.